CoT
Chain of Thought
一文读懂:大模型思维链 CoT(Chain of Thought) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
RAG
检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation - RAG)
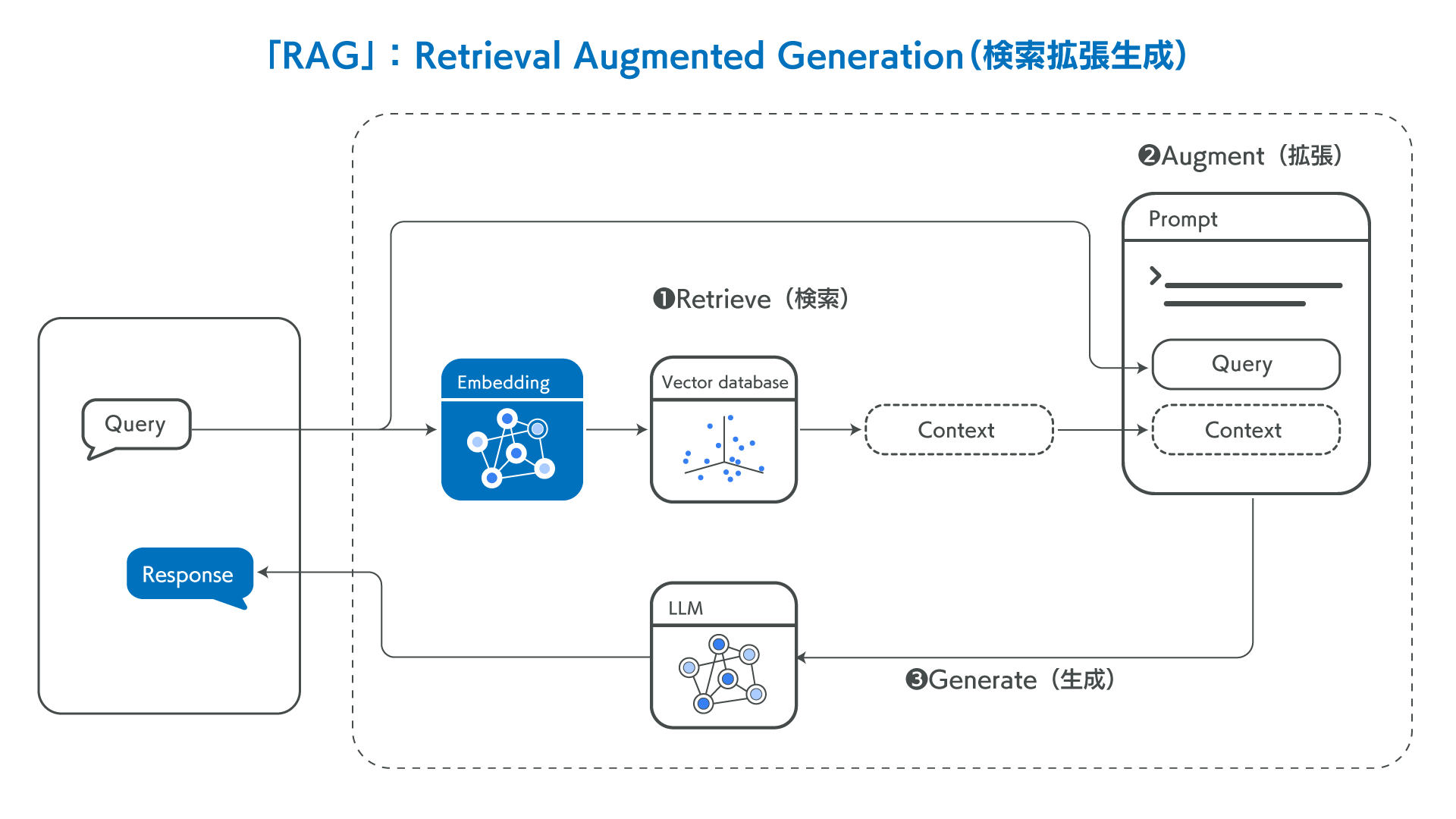
相关优缺点
什么是检索增强生成 (RAG)?| RAG 全面指南 | Elastic
法律QA系统RAG实例
本节将利用92k 带有法律依据的情景问答数据 LawGPT_zh (选自 LexiLaw)作为 RAG 的主要知识来源,使用 Elasticsearch 作为向量数据库存储对应的 question、reference 和 answer,并且采用 bert-base-chinese 作为嵌入模型,为每一个字段编码得到768维的语义向量。在检索时,利用余弦相似度匹配相关的问题,并返回所有字段作为 prompt,利用 OpenAI API传入 GPT4 大模型以供参考。
🔔源码:https://github.com/SlieFamily/RagLaw-GptWeb
数据库填充
首先在官网下载对应的 Elasticsearch 服务端程序,并启动。
默认情况下,与服务器进行http通信的方式是套接字 127.0.0.1:9200。这个部分可以在Elasticsearch 应用程序安装目录下的 conf\elasticsearch.yml 配置文件中修改。
然后将数据集放入项目文件夹下的 /data内,并运行 app.py 中的 init_ES() 函数。应保证 app.py 中接入 ES 服务器的 IP及端口号 与前面配置的对应。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| class ProcessIntoES:
def __init__(self):
self._index = "crime_data"
self.es = Elasticsearch([{"host": "127.0.0.1", "port": 9200, 'scheme': 'http'}])
self.doc_type = "crime"
cur = '/'.join(os.path.abspath(__file__).split('/')[:-1])
self.music_file = os.path.join(cur, 'data/qa_with_ref_92k.json')
'''创建ES索引,确定分词类型'''
def create_mapping(self):
node_mappings = {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"question": { "type": "text" },
"answer": { "type": "text" },
"reference": { "type": "text" },
"question_embedding": {"type": "dense_vector", "dims": 768},
"answer_embedding": {"type": "dense_vector", "dims": 768},
"reference_embeddings": {"type": "dense_vector", "dims": 768},
}
}
}
if not self.es.indices.exists(index=self._index):
self.es.indices.create(index=self._index, body=node_mappings)
print("Create {} mapping successfully.".format(self._index))
else:
print("index({}) already exists.".format(self._index))
'''批量插入数据'''
def insert_data_bulk(self, action_list):
success, _ = bulk(self.es, action_list, index=self._index, raise_on_error=True)
print("Performed {0} actions. _: {1}".format(success, _))
'''初始化ES,将数据插入到ES数据库当中'''
def init_ES():
pie = ProcessIntoES()
pie.create_mapping()
start_time = time.time()
index = 0
count = 0
action_list = []
BULK_COUNT = 100
with open(pie.music_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
data = json.load(file)
for doc in data:
doc["question_embedding"] = encode_texts([doc["question"]])[0]
doc["answer_embedding"] = encode_texts([doc["answer"]])[0]
doc["reference_embeddings"] = encode_texts(doc["reference"])[0]
index += 1
action = {
"_index": pie._index,
"_source": doc,
}
action_list.append(action)
if index > BULK_COUNT:
pie.insert_data_bulk(action_list=action_list)
index = 0
count += 1
print(f'-----embedded {count}00 QA pairs-----')
action_list = []
end_time = time.time()
print("Time Cost:{0}".format(end_time - start_time))
print(f'processing {index}% for {count}')
if __name__ == "__main__":
init_ES()
|
提示词构建
本项目整体遵从 RAG 技术的逻辑,程序获取到用户的输入后,将其再次利用bert-base-chinese 进行编码,然后通过余弦相似度和数据库内的向量内容进行匹配,以找到更相关的原始知识内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
def search_similar_documents(question, top_k=5):
query_vector = encode_texts(question)[0]
query = {
"size": top_k,
"_source": ["question", "answer", "reference"],
"query": {
"script_score": {
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"script": {
"source": """
double maxCosineSimilarity = 0;
maxCosineSimilarity = Math.max(maxCosineSimilarity, cosineSimilarity(params.query_vector, 'question_embedding'));
maxCosineSimilarity = Math.max(maxCosineSimilarity, cosineSimilarity(params.query_vector, 'answer_embedding'));
maxCosineSimilarity = Math.max(maxCosineSimilarity, cosineSimilarity(params.query_vector, 'reference_embeddings'));
return maxCosineSimilarity + 1.0;
""",
"params": {
"query_vector": query_vector
}
}
}
}
}
pie = ProcessIntoES()
response = pie.es.search(index=pie._index, body=query)
hits = response["hits"]["hits"]
return [hit["_source"] for hit in hits]
|
将获取得到的 Python List 格式的 top_k 条相关内容拼接起来作为字符串返回:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| def convert_documents_to_string(docs):
content = ""
for doc in docs:
content += "related question:"+doc['question']+"\n"
content += "reference:"
for ref in doc['reference']:
content += ref+"\n"
content += "answer:"+doc['answer']+"\n"
content += "\n"
return content
|
内容再以如下格式组成提示词:
1
| {"role": "system", "content": f"通过检索可以得到以下相关内容:\n{context}"}
|
对话工作流
当所有数据编码入库后,即可注释掉 init_ES(),直接运行 app.py 开始对话。注意,app.py 中应该明确填充好开发者申请得到的 OPENAI_API_KEY 才能正常调用大模型进行对话。
具体来说,整个对话的工作流如下。利用 OPENAI_API_KEY 访问指定的模型,如 gpt-3.5-turbo,然后以字典列表的方式将输入和提示词通过 API 传入模型,然后再以流式的方式返回给用户。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| def qa_interface(question, docs):
context = convert_documents_to_string(docs)
role_msg = {"role": "user", "content": question}
prompt_msg = {"role": "system", "content": f"通过检索可以得到以下相关内容:\n{context}"}
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful Chinese law assistant."},
]
messages.append(role_msg)
messages.append(prompt_msg)
stream = client.chat.completions.create(
model='gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages=messages,
stream=True,
temperature=0.7,
)
assistant_message = ""
for chunk in stream:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content is not None:
chunk_message = chunk.choices[0].delta.content
assistant_message += chunk_message
print(chunk_message, end="", flush=True)
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_message})
print()
print('ref:\n'+context)
if __name__ == "__main__":
while True:
print('-'*20)
print('-> 请输入问题:', end="")
question = input()
print('-'*20)
print('◇ 检索相关内容并生成回答....\n')
docs = search_similar_documents(question, top_k=3)
qa_interface(question, docs)
|
参考
- 提示工程指南 | Prompt Engineering Guide (promptingguide.ai)
- 什么是检索增强生成 (RAG)?| RAG 全面指南 | Elastic
- ElasticSearch入门篇(保姆级教程) - coderxz - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
- Elasticsearch:什么是检索增强生成 - RAG?检索增强生成(rag)-CSDN博客